The Scientific Research Behind Cane Sugar Processing: Just How Sweet Taste is Refined
The Scientific Research Behind Cane Sugar Processing: Just How Sweet Taste is Refined
Blog Article
A Thorough Overview to the Ecological Influence and Sustainability Practices in Cane Sugar Processing
The environmental influence of walking cane sugar handling provides a complex selection of obstacles that warrant cautious examination. From dirt deterioration and extreme water use to the carbon impact associated with farming and manufacturing, the consequences of traditional techniques are significant. What specific techniques can be executed to strike a balance in between productivity and ecological stewardship?
Summary of Cane Sugar Handling
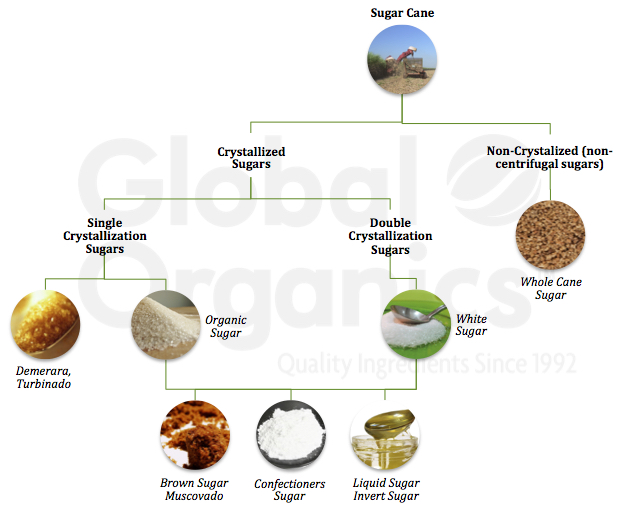
Cane sugar handling involves a collection of methodical actions that transform sugarcane right into refined sugar. Originally, harvested sugarcane is carried to refining facilities, where it undertakes cleaning up to get rid of soil and particles. Following this, the cane is squashed to extract juice, which is after that clarified by getting rid of impurities via heating and the enhancement of lime.
The cleared up juice undertakes evaporation, where water is gotten rid of to concentrate the sugar material. This focused syrup is then taken shape via air conditioning, allowing sugar crystals to develop. These crystals are divided from the staying syrup utilizing centrifugation, resulting in raw sugar. To accomplish polished sugar, the raw item undergoes additional purification procedures, which might include filtering system and cleaning to eliminate staying pollutants and shade.
The final item is after that dried and packaged for distribution. Throughout this entire procedure, keeping performance and quality assurance is necessary to guarantee the sugar satisfies sector requirements. Each action in cane sugar processing not only contributes to the final product but also has implications for resource usage and waste generation, establishing the stage for discussions on sustainability and environmental effects linked with sugar production.
Environmental Obstacles of Production
The manufacturing of walking cane sugar presents several significant ecological obstacles that warrant focus. One key problem is the considerable usage of agrochemicals, consisting of pesticides and fertilizers, which can lead to soil deterioration, biodiversity loss, and contamination of local water resources. The overflow from sugarcane fields usually lugs these chemicals into nearby communities, disrupting aquatic life and influencing the wellness of communities reliant on these water bodies.
An additional obstacle is the high energy consumption linked with sugarcane handling. The boiling and refining stages call for significant warm, primarily produced by burning nonrenewable fuel sources, adding to greenhouse gas discharges. Additionally, the large acreage required for sugarcane growing can result in deforestation and habitat destruction, more worsening climate adjustment and threatening wild animals.
Furthermore, the labor techniques in some areas raise honest issues, as employees may encounter bad working problems and insufficient salaries. This scenario commonly perpetuates a cycle of hardship in local neighborhoods. Cane Sugar Processing. Dealing with these ecological challenges is critical for establishing more lasting practices in walking stick sugar production, ultimately profiting both the environment and the areas involved in this market
Water and Land Usage Impact
Water sources and land utilization are important components in the walking cane sugar industry that dramatically affect the setting. The cultivation of sugarcane needs significant water input, with estimates recommending that it can eat up to 2,000 liters of water per kg of sugar generated. This intensive use of water usually causes deficiency Check Out Your URL of local water resources, influencing not only the sugarcane plantations however additionally surrounding ecological communities and areas that depend on the same water resources for agriculture and domestic usage.

Additionally, land usage for sugarcane growing can lead to logging and the conversion of all-natural environments into monoculture vineyards. This practice reduces biodiversity, disrupts regional ecosystems, and contributes to dirt degradation. The growth of sugarcane areas typically trespasses on valuable agricultural land, developing competition for resources in between food and biofuel manufacturing.
Sustainable methods, such as maximizing irrigation methods and applying plant rotation, are vital to minimize these impacts. By embracing a lot more reliable water use and land administration methods, the walking cane sugar industry can decrease its ecological impact, making sure an equilibrium in between farming productivity and environmental preservation.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas discharges stand for a significant environmental worry within the walking cane sugar handling market, especially as farming techniques increase to fulfill international need. The growing of sugarcane, a plant that prospers in exotic environments, counts greatly on artificial plant foods and chemicals, which add to laughing gas discharges. Furthermore, land-use changes, including deforestation for new sugarcane plantations, release co2 saved in plant life and soil.
Throughout handling, power intake is one more major resource of greenhouse gas discharges - Cane Sugar Processing. Many sugar mills make use of fossil fuels to power address equipment and create warmth, causing significant carbon footprints. In addition, the transportation of raw sugarcane and completed products adds layers of discharges through fuel burning in vehicles
This involves evaluating current farming techniques, processing methods, and transport systems to identify locations for improvement and reduction. Attending to greenhouse gas discharges is crucial for cultivating a more lasting walking stick sugar sector in a transforming environment.
Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Sustainable practices and developments are significantly vital in the cane sugar handling sector as stakeholders look for to reduce environmental effects while maintaining performance. One considerable improvement is the implementation of incorporated plant management, which maximizes source use by incorporating soil administration, bug control, and plant turning techniques. This method enhances yield while minimizing chemical inputs and protecting soil health.
In addition, the fostering of eco-friendly energy resources, such as biomass from sugarcane deposits, has acquired traction - Cane Sugar Processing. By transforming waste products right into energy, refining facilities can minimize their reliance on fossil gas, therefore lowering greenhouse gas exhausts
Water management practices have also seen renovations with the recycling and reusing of water in processing plants, substantially decreasing freshwater consumption. Advancements in technology, such as accuracy farming, make it possible for farmers to monitor crop health and source use more efficiently, making certain lasting farming techniques.
Moreover, accreditation programs like Fair Trade find out this here and Jungle Partnership encourage eco accountable farming methods and promote social equity within the supply chain. By embracing these lasting practices and advancements, the cane sugar processing market can boost its durability and contribute positively to environmental stewardship.
Final Thought
The ecological influence of walking cane sugar processing presents substantial obstacles, consisting of soil deterioration, high water intake, and greenhouse gas emissions, along with ethical worries connected to labor practices. Addressing these concerns via sustainable techniques, such as incorporated plant management, renewable resource adoption, and water recycling, is vital. By advertising environmentally accountable and socially equitable approaches in sugar production, the industry can minimize its negative impacts, making sure a much more sustainable future for both neighborhoods and communities associated with this market.
Walking cane sugar processing entails a series of systematic actions that transform sugarcane right into refined sugar. Each action in walking stick sugar processing not only adds to the final item but additionally has ramifications for source use and waste generation, establishing the stage for conversations on sustainability and environmental influences connected with sugar manufacturing.
Greenhouse gas emissions stand for a significant ecological concern within the walking cane sugar processing market, particularly as farming practices broaden to fulfill global need.Sustainable methods and innovations are significantly vital in the walking stick sugar processing industry as stakeholders seek to lower environmental effects while keeping productivity.The ecological influence of cane sugar processing offers significant difficulties, consisting of dirt degradation, high water usage, and greenhouse gas discharges, along with honest worries related to labor practices.
Report this page